MEMS Vibration Sensors

What is the MEMS sensor?
The term MEMS refers to micro-electro-mechanical systems. This means that MEMS are systems with components as small as 1 to 100 microns in size, and these systems can reach an average size of 20 microns to 1 millimeter. Like any integrated circuit, MEMS are manufactured with what is known as silicon wafers.
MEMS sensor for condition monitoring
When used as vibration sensors, the MEMS operate on the same principle as the accelerometers used in cell phones for screen rotation functionality. These accelerometers have a seismic mass attached to the housing, which uses the flexibility of the silicon to move back and forth when changes are detected in the orientation of the cell phone. When the seismic mass moves, it generates a current flow that is correlated to the acceleration. In this way, the movement of the seismic mass is measured and used to calculate the orientation.
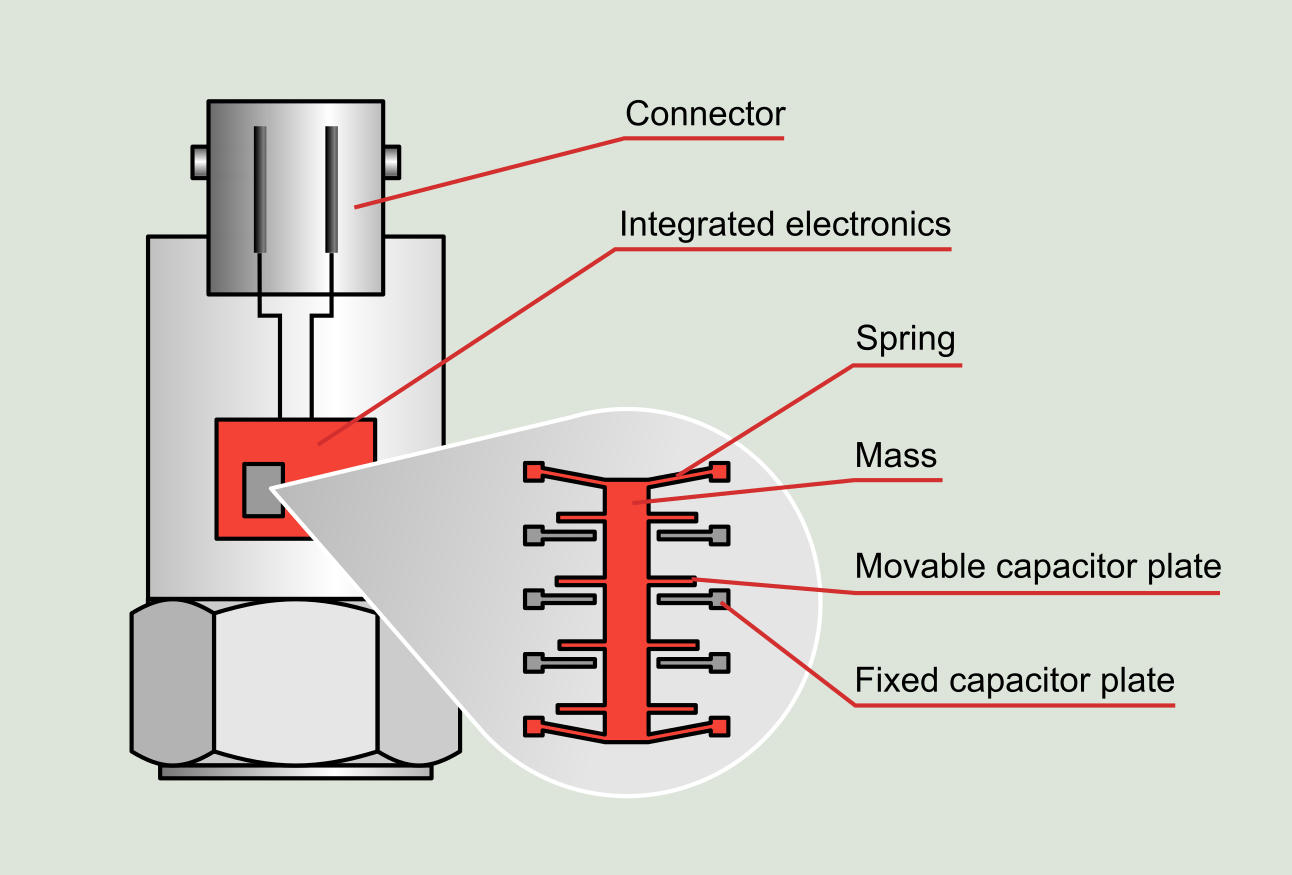
The MEMS used to measure vibrations can be either variable capacitive or piezo-resistive. Like the operating principle described above, the repetitive movements of the vibrations generate changes in capacitance or resistance depending on the type of MEMS, and these changes will be correlated with acceleration values. These sensors are often used for low frequencies reaching up to 1,000 HZ.
An interesting fact about these micro-systems is how engineers and scientists managed to use the same manufacturing methods like the ones used to fabricate integrated circuits. This made it possible to connect these electro-mechanical micro-systems to electronic circuits in the same chip. Although they may sound a very new technology, MEMS were first introduced in the 60s, and initially commercialized during the 80s in applications for inkjet printers.
Other MEMS applications
- Automotive applications, such as crash detection for the correct operation of airbags
- Navigation systems for different types of vehicles, including drones, aircrafts, helicopters, and submarines - to name a few
- Consumer electronic device applications, such as blocking systems for laptop hard drives to avoid data loss or damage, in case a free fall is detected
- Pressure sensors for car tires
- Others
Owing to the high degree of sensitivity of MEMS in detecting changes in orientation (movement), engineers and scientists involved in the development of condition monitoring technologies decided to use them in vibration measuring devices. In this way, any low-frequency vibration out of the range of ICP sensors can be easily detected.
Benefits of MEMS vibration sensors for predictive maintenance
Of course, any new technology has its benefits and limitations. Among the main benefits of MEMS vibration sensors for predictive maintenance are the following:
-
Higher accuracy and repeatability
-
Real-time measurement to better access and transmit data
-
Measurement at very low frequencies
-
Higher reliability
-
Relatively low cost
-
Continuous wireless data collection because of very low energy consumption
Limitations of MEMS vibration sensors for predictive maintenance
On the other hand, the main problem with MEMS sensors is that they are unable to measure vibrations in frequencies beyond 1,000 Hz and are also limited to an operating temperature of 110ºC. This can sometimes be a hassle, depending on the machine, in which case the piezo-electric sensor is recommended.
However, with continuous technological advances, these limitations should eventually be overcome.
What is Power-MI?
Power-MI is a cloud based solution that allows you to design & manage your condition-based maintenance plan integrating all techniques into one platform. Easy reporting, automatic work orders and CMMS integration.
Read more